When you connect to a VPN, all of your internet traffic is routed through an encrypted “tunnel” between your computer and the VPN server.
 Checkout this video:
Checkout this video:
Introduction
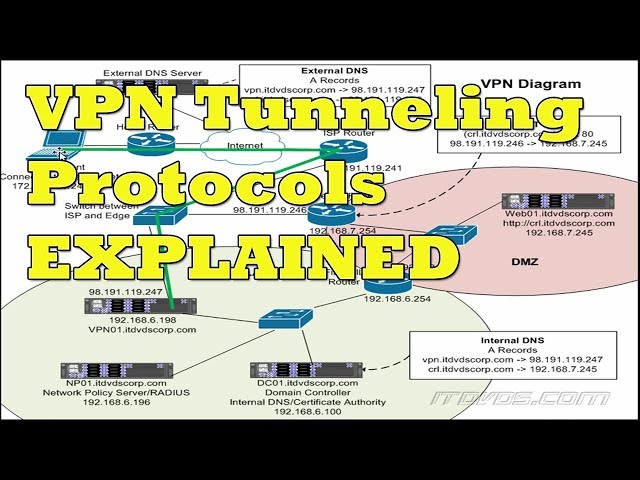
In computer networks, a tunneling protocol is a communications protocol that allows for the secure movement of data from one network to another. A tunnel is created when a tunneling protocol is used to encapsulate data within the headers of other protocols. This process allows for the secure transmission of data between two networks that would otherwise be unable to communicate with each other.
There are a number of different tunneling protocols that can be used, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common tunneling protocols are PPTP, L2TP, and IPsec.
PPTP is the oldest and most well-known tunneling protocol. PPTP uses a Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) to encapsulate data within IP packets. PPP is used because it is able to provide encryption and compression, two features that are important for VPNs. PPTP has been widely used in the past, but it has a number of security vulnerabilities that have been exploited by hackers. For this reason, PPTP is not considered to be as secure as some of the other tunneling protocols.
L2TP is a newer tunneling protocol that was developed to address the security vulnerabilities of PPTP. L2TP uses IPSec for encryption and authentication, which makes it more secure than PPTP. However, L2TP is more complex than PPTP and can be more difficult to configure.
IPsec is a suite of protocols that can be used for authentication and encryption. IPsec is often used in conjunction with other protocols, such as L2TP, to provide a more complete solution for VPNs. IPsec has a number of advantages over other encryption methods, including increased security and compatibility with a variety of devices and operating systems.
What is Tunneling?
In computer networks, tunneling is the process of sending data from one network to another. This can be done for a variety of reasons, such as to increase security or to bypass restrictive firewalls.
Tunneling is accomplished by encapsulating data in a layer that is then sent to the other network. This layer is usually an encryption protocol, such as Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS).
Once the data reaches the other network, it is decrypted and forwarded to its final destination. Tunneling can be used to create virtual private networks (VPNs), which allow users to securely connect to a remote network.
VPNs are often used by businesses to allow employees to access company resources remotely. They can also be used by individuals to bypass censorship or content restrictions imposed by government entities or internet service providers (ISPs).
How is Tunneling Accomplished in a VPN?
Tunneling is the process of sending data through a public network, such as the Internet, using a private network, such as a VPN. When data is tunneled, it is encrypted so that only the sender and receiver can access it. This process helps to keep data safe and secure as it travels between the two points.
The Steps Involved in Tunneling
In computer networks, tunneling is the process of sending data from one network to another. This is done by encapsulating the data in such a way that it can be transmitted over the network. In a virtual private network (VPN), tunneling is used to send data from a public network (such as the Internet) to a private network (such as a company’s internal network).
There are two steps involved in tunneling: encrypting the data and encapsulating the data. Encrypting the data ensures that it cannot be read by anyone who does not have the proper key. Encapsulating the data ensures that it can be transmitted over the network.
Conclusion
Tunneling is the process of sending data from one computer to another over an untrusted network. The data is encrypted at the sender and decrypted at the receiver. This protects the data from being read or modified by anyone other than the intended recipient.
VPNs use tunneling to send data over public networks, such as the Internet. This allows VPN users to securely access resources on private networks, such as a company’s internal network or a home network.
Tunneling is accomplished by encapsulating data in aprotocol that is not native to the untrusted network. For example, tunneling Internet Protocol (IP) traffic over public networks uses aprotocol called Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE). GRE encapsulates IP packets in order to send them over non-IP networks, such as Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) or Frame Relay.
Another common protocol used for VPN tunneling is Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). SSL encrypts and authenticates data that is sent over the Internet using Transport Layer Security (TLS). TLS is a successor to SSL and provides better security than SSL.
